|
Cryptosporidium hominis TU502
|
[ Alveolata | Apicomplexa | Conoidasida | . . .
. . . | Cryptosporidiidae | Cryptosporidium | Cryptosporidium hominis ]
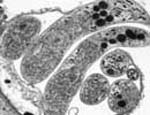 Courtesy of Saul Tzipori, Tufts
Courtesy of Saul Tzipori, Tufts
|
| Taxonomy: | Eukaryota | Alveolata | Apicomplexa | Conoidasida | Coccidia | Eucoccidiorida | Eimeriorina | Cryptosporidiidae | Cryptosporidium | Cryptosporidium hominis |
| Comment: | Cryptosporidium hominis is the dominant species which infects humans. Although generally self-limiting, this disease can cause fatalities in children and immunocompromised adults. The genome sequence of Cryptosporidium hominis shows features consistent with its life cycle as an obligate parasite. This organism lacks the genes necessary for the production of a number of biochemical building block such as nucleotides and amino acids. To compensate for this lack, the genome contains a large number of transporter or transporter-like genes. |
|
|

|
Go to NCBI Taxonomy (353151) |
|
|
|  |
Encyclopedia of life |
|
|  |
Wikipedia |
| Publications: |
Ifeonu OO, Chibucos MC, Orvis J et. al. 
( 2016)
Pathog Dis 74.

Xu P, Widmer G, Wang Y et. al. 
( 2004)
Nature 431, 1107-12.

|
Genome files
|
 Courtesy of Saul Tzipori, Tufts
Courtesy of Saul Tzipori, Tufts










